Polymethyl methacrylate, abbreviated as PMMA, is an important injection molding thermoplastic that was developed in the earlier stage. The plastic features great transparency, chemical stability and weather resistance. It is easy to dye and process, with an aesthetic appearance, thus widely applied in the construction industry.
Chemical Formula: [C5O2H8]n
Structural Formula:
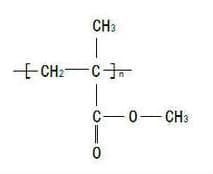
PMMA, an important thermoplastic developed in the early days, is commonly known as plexiglass or acrylic, of which the chemical name is polymethyl methacrylate. The material features outstanding transparency, chemical stability and weather resistance.
PMMA is a highly transparent amorphous thermoplastic polymer with a relative density (30℃) of 1.188-1.22. Its High transparency, with the light transmittance of 90%-92%, is even higher than that of inorganic glass; its refractive index is 1.49. It is mechanically strong, with the tensile strength of 60-75MPa, and impact strength of 12-13kJ/m, 8-10 times higher than that of inorganic glass. It is able to be stretched and oriented, allowing its impact strength to increase by 1.5 times. It boasts excellent resistance to ultraviolet rays and atmospheric aging. Its glass transition temperature is 80-100℃, the decomposition temperature is > 200℃, and the service temperature is 40-80℃. It is resistant to alkali, dilute acid, water-soluble inorganic salts, alkanes and grease; soluble in dichloroethane, chloroform, acetone, acetic acid, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran and ethyl acetate, etc.; and insoluble in ethanol, ether and petroleum ether, etc., with good electrical insulation.

PMMA boasts the advantages of light weight, low price, and easy for injection molding.
Optical Property
The most prominent feature of PMMA is its excellent optical property, which is also why it is referred to as “plexiglass”. The refractive index of PMMA is 1.49, with a light transmittance of 92%.
Mechanical Property
(1). Higher tensile strength and elastic modulus: its impact strength is 7-18 times that of inorganic glass, and its toughness is higher than that of PS, but much lower than that of ABS. It is brittle to some extent, so tends to break under high impact.
(2). With an insufficient surface hardness, it is easy to be scratched or rubbed by hard objects and thus loses gloss.
Thermal Property
(1). It is a flammable material, and after being ignited, cannot be self-extinguished when the fire is removed. The flame is light blue with a white lower part. While burning, it generates the smell of rotten fruits and vegetables.
(2). Its TG is 105℃, softening point is 100-102℃, and catalytic temperature is below -60℃. The long-time service temperature of PMMA ranges between -60 and 65℃, and the short-term service temperature should not exceed 105℃.
(3). Its specific heat capacity is lower than that of most thermoplastics, which is conducive to its rapid plasticization by heating.
Chemical Property
(1). Chemical Resistance
PMMA is resistant to water-soluble salts, weak bases and certain dilute acids, but not to oxidizing acids or strong bases. At the same time, the greater the concentration of the medium and the higher the temperature, the lower its stability becomes.
Among all organic compounds, PMMA is more stable to long-chain alkanes, simple ethers, oils and fats, but not resistant to short-chain alkanes, alcohols and ketones, etc.
(2). Weather Resistance
Compared with other resins, PMMA boasts excellent weather resistance. Aging is mainly caused by the effect of ultraviolet rays. Under outdoor atmospheric conditions, its performance only declines slightly.
- Electrical Property
Although the macromolecular chain of PMMA is similar to that of PE, its electrical property is much worse than that of the latter. However, since the polarity of the ester group is not too high, it still has excellent dielectric and electrical insulation properties.
PMMA Processing Techniques
- Casting: used for production of such profiles as plexiglass sheets and bars, that is, producing profiles through bulk polymerization.
- Injection Molding: the pellets prepared through suspension polymerization are molded by a common plunger or screw injection molding machine.
- Extrusion: the pellets produced through suspension polymerization is used to produce plexiglass panels, bars, pipes and sheets, etc. However, due to the small molecular weight of the polymer, the mechanical properties, heat resistance and solvent resistance of the profiles made this way, especially the sheets, are inferior to those produced via casting, but its advantage lies in the high production efficiency.
- Thermoforming: referring to the process of making plexiglass panels or sheets into products of various sizes and shapes – clamp the blank cut to the required size on the mold frame, soften it by heating, and then press it tightly against the mold surface, to obtain the same shape as the molding surface; after cooling and solidifying, trim the edges to get the final product.
Plastic Injection Molding Conditions of PMMA

- Drying: The drying temperature should be 10-20℃ (100-110℃) lower than its heat deformation temperature, while the drying time is about 2-8 hours (drying the water content to 0.02-0.04%). The dried material cannot be exposed to air, but should be kept in a closed hopper.
- Injection Temperature: 180-220℃;
- Injection Pressure: 80-130MPa;
- Mold Temperature: 40-60℃.
- The mold runner should be wide and short, and the pinpoint gate should be avoided, otherwise the gate diameter should be no less than 1.5mm
- Usually, the product should be heat treated to eliminate internal stress.
