1. A Brief Introduction of ABS
Abbr.: ABS
Full Name: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
As one of the five synthetic resins, the ABS plastic boasts excellent resistance to impact, heat, low temperature and chemicals, as well as outstanding electrical properties, in addition to the characteristics of easy processing, stable product dimensions, and great surface gloss. It is easy to paint and color, and allows for secondary processing such as metal spraying on the surface, electroplating, welding, thermal pressing and bonding. As a versatile engineering thermoplastic, it is widely used in such industrial fields as machinery, automobile, electronics & appliances, instruments, textiles, and construction.

ABS is mostly used in the automotive, electronics & appliances and building material industries, while its applications in the automotive field include automotive instrument panel, body panel, interior trim panel, steering wheel, sound insulation panel, door lock, bumper, ventilation pipes, and many more. In terms of electrical appliances, it is extensively used in such electronics and appliances as refrigerator, television, washing machine, air conditioner and computer. In terms of building materials, ABS pipes, ABS sanitary ware, and ABS decorative panels are commonly used in the construction industry. Furthermore, ABS is also broadly used in packaging, furniture, sports & entertainment products, machinery and instrument industries.
2. ABS Components:
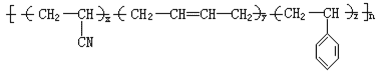
ABS is synthesized from three chemical monomers – acrylonitrile (C3H3N), butadiene (C4H6) and styrene (C8H8), each of which possesses different characteristics: acrylonitrile is highly strong, and thermally and chemically stable; butadiene features great toughness and impact resistance; styrene is characterized by easy processing, high gloss and strength. From the morphological point of view, the ABS resin is an amorphous material.
Structural Formula:
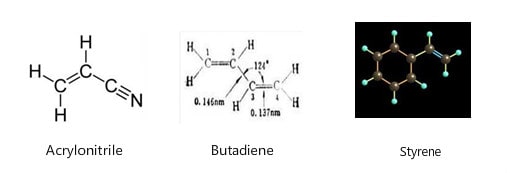
The characters from three chemical monomers
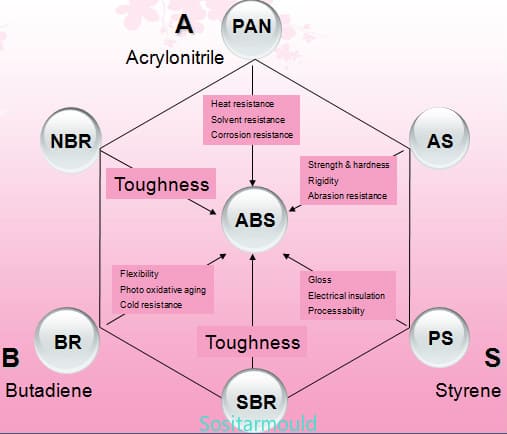
3. ABS Characteristics:

1. Color:
ABS is light yellow opaque pellets with high surface gloss.
2. Specific Gravity:
The specific gravity of ABS is 1.05 g/cm3, slightly heavier than water. It possesses the characteristics of high toughness, hardness and rigidity.
3. Combustion Characteristics:
ABS burns relatively slowly, and is able to continue burning after fire is removed. The flame is yellow with black smoke. After burning, it softens, without melting and dripping, but emits a special cinnamon smell.
4. ABS Properties:
1. ABS is opaque and ivory-colored pellets, of which the products can be dyed in five colors, with gloss as high as 90%. ABS combines well with other materials, and is easy to surface print, coat and plate. As a flammable polymer, ABS has an oxygen index of 18.2. Its flame is yellow, with black smoke, charred but without dripping, while emitting a special cinnamon smell;
2. ABS boasts excellent mechanical properties. Its outstanding impact strength allows it to be used under extremely low temperature conditions; ABS is highly wear resistant, dimensionally stable, and oil resistant, thus able to be used for bearings under moderate loads and speeds. The creep resistance of ABS is greater than that of PSF and PC, but lower than that PA and POM. Among all plastics, ABS features lower bending strength and compressive strength. The mechanical properties of ABS are greatly affected by temperature;
3. The heat distortion temperature of ABS is 93-118℃, and after annealing, that of its product can be increased by about 10℃. ABS still shows a certain degree of toughness at -40℃, allowing it to be used under the -40-100℃ temperature conditions;
4. ABS boasts great electrical insulation and is hardly affected by temperature, humidity and frequency, so it can be used in most environments;
5. ABS is not affected by water, inorganic salts, alkalis and various acids, but it is soluble in ketones, aldehydes and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Stress cracking will be caused when ABS is eroded by glacial acetic acid and vegetable oil, etc. The poor weather resistance of ABS makes it prone to degradation under the influence of ultraviolet light; after outdoor application for half a year, its impact strength drops by half.
5. Types of ABS Plastics:
According to impact strength, ABS can be classified into: super high impact, high impact, medium impact and other varieties.
According to forming process, ABS can be classified into: injection molded, extruded, calendered, vacuum and blow molded, as well as other varieties.
According to application and performance features, ABS can be classified into: general-purpose, heat-resistant, electroplated, flame retardant, transparent, antistatic, sheet, pipe and other varieties.
6.
Injection Molding Conditions of ABS:
1. Drying Treatment: ABS material is hygroscopic and requires to be dried before processing. Suggested drying conditions: 80-90℃ for no less than 2 hours.
2. Melting Temperature: 210-280℃; suggested temperature: 245℃.
3. Mold Temperature: 25-70℃. (Mold temperature affects the surface gloss of the plastic part; the lower the temperature, the lower the gloss).
5. Injection Pressure: 500-1000bar.
6. Injection Speed: medium and high speed.
7. ABS products are easy to carry static electricity, and the surface is easy to attract dust.
8. Its shrinkage ranges between 4‰ and 8‰.
