Product ejection is the last step in the plastic injection molding process. After a product solidifies in the mold, an effective method is needed to eject it from the mold. Product ejection cannot be neglected, and during the ejection process, the product should be protected from deformation, ejector marks, cracking and other damages. So, this is where the ejection system – which falls into the following categories – comes in:
1. Round Ejector Pin 2.Ejector blade(Rectangular Ejector ) 3.Ejector Sleeve
4. Ejector Block 5.Stripper Plate 6.Lifter 7. Air Ejection
Ejection System design principles
The following principles should be observed during ejector system design:
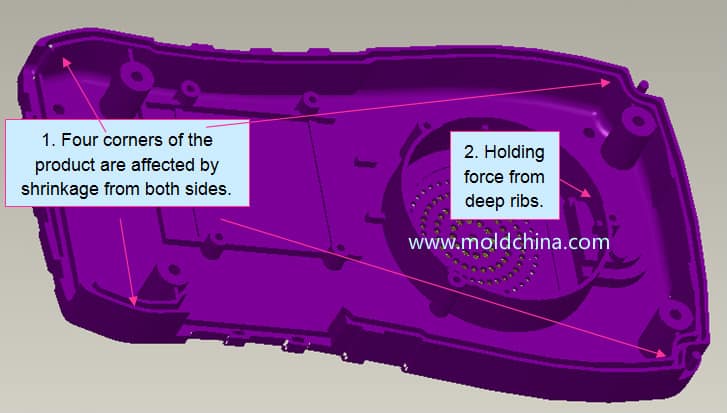
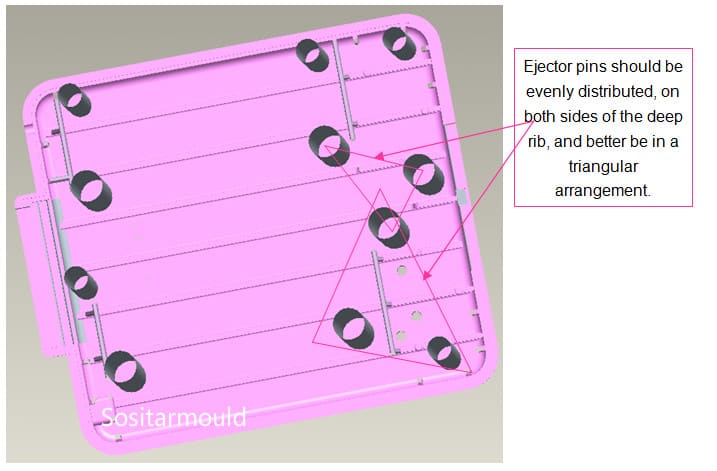
(1). To protect the product from deformation, cracking, or perforation caused by ejection, the ejectors should act on the part where the product is able to withstand the maximum force, i.e., the part with great rigidity, such as the rib, flange, and wall edge of the shell-shaped products.
(2). In order to avoid ejector marks that affect the appearance of a product, the ejector system should be located on the hidden surface or non-decorative surface of the product. Especially for transparent products, attention should be paid to the selection of ejector position and type.
(3). The ejector stroke is usually 5-10mm after the product is released from the mold. For simple and large products, the ejector stroke is 2/3 of the product depth.
(4). Usually, the end surface of the ejector pin is 0.05-0.1mm lower or higher than mold cavity surface.
Product holding force
Product ejector force is greater than the holding force that is caused by product shrinkage.
The types of ejection system
1. Round Ejector Pin
Round Ejector Pin: As the most common and simple ejector, a round ejector pin and the hole are easy to machine, so they are widely applied as standard parts.

Pros:
Easy manufacturing and machining;
Little resistance;
Convenient maintenance.
Cons:
There are certain limitations on ejector location.
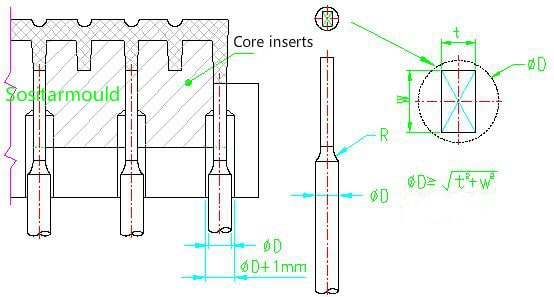
2. Ejector blade
Ejector blade (Rectangular Ejector): When the finished product features a smaller space and a deeper rib, which makes it hard to arrange the round ejector pin, the flat-top rectangular ejector pin is used instead, which is usually located at the bottom of the rib of the finished product. Rectangular ejector pin holes are usually machined by wire cutting, and the pins need to be quenched to make it sufficiently strong and wear resistant.

Cons: Difficult machining, easy to wear, and high cost
3. Ejector Sleeve
The ejector sleeve is a hollow ejector pin. The ejector sleeve is used in combination with the ejector pin, referred to as the sleeve pin set, which is one of the accessories of a plastic injection mold. The ejector sleeve is a mechanism that has to be adopted when there is a circular through hole or blind hole on the product required to be ejected. It consists of a sleeve and a pin. The sleeve is installed on the ejector plate, while the pin is installed on the base plate. After the mold is opened, the sleeve ejects the product wrapped around the pin.
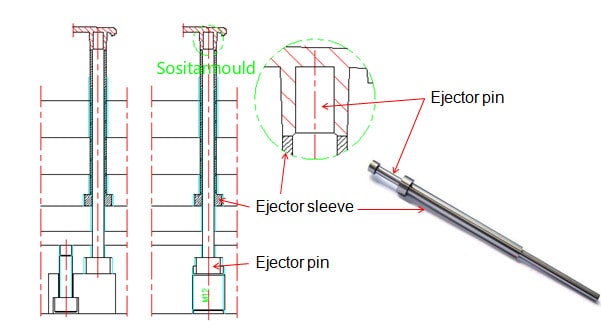
Commonly used to eject elongated bolts and cylindrical parts.
Pros: Large and uniform ejector force, without obvious marks.
Cons: Difficult manufacturing and assembly, easy to wear and tear, and high cost.
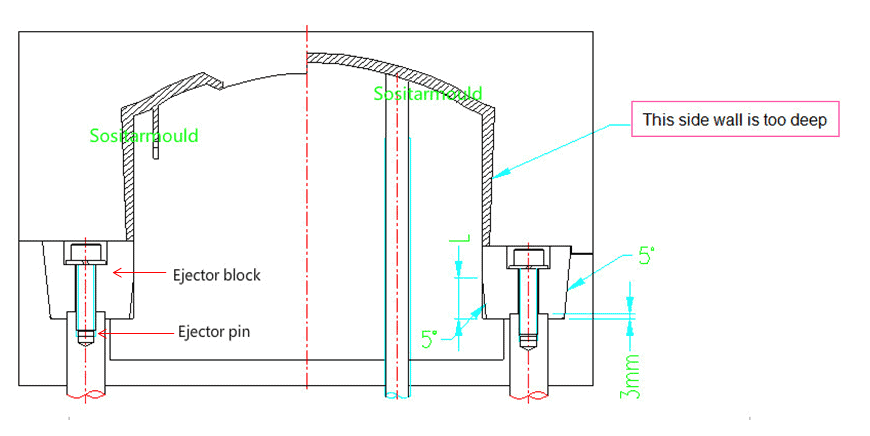
4.Ejector Block
In some molds, since the side wall of the finished product is too deep, it is easy to wrap around the mold core and produce a large mold release force. To make it easy for mold release, the ejector structure that combines the ejector block and the ejector pin is used.
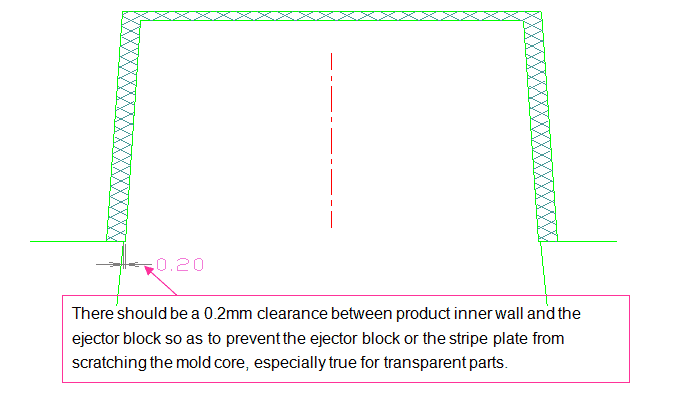
5. Striper Plate
Striper plate is suitable for the ejection of cylindrical plastic parts, thin-walled containers and various shell-shaped plastic products. The main feature of this ejector mechanism is that the ejector force is high, uniform and stable, and the plastic parts are not prone to deformation, without ejector marks on the surface. Also, the structure is simpler than that of the ejector sleeve, and there is no need for a resetter, because the ejector mechanism can be reset by the thrust of the mold parting surface on the cavity plate when the mold closes.
Cons: Complicated mold structure, and high manufacturing cost.
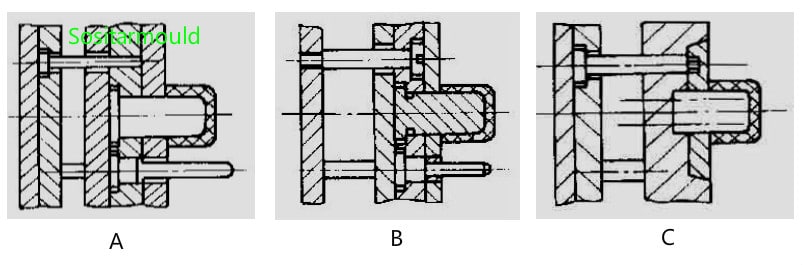
A. Commonly used type B. Distance screw holds the ejector plate C. Ejector plate is inserted into the core plate
Figure A shows the most common type. The ejector pin pushes the ejector plate to eject the plastic part out of the core. The ejector plate is guided by the guide pins in the guiding mechanism of the mold core and the mold cavity.
Figure B shows that the ejector plate is held by the distance screw to prevent it from falling off.
Figure C shows that the ejector plate is inserted into the core plate, also known as the ring-shaped ejector plate. The mold features a compact structure, and the inclined surface on the ejector plate is to facilitate its reset when the mold closes.
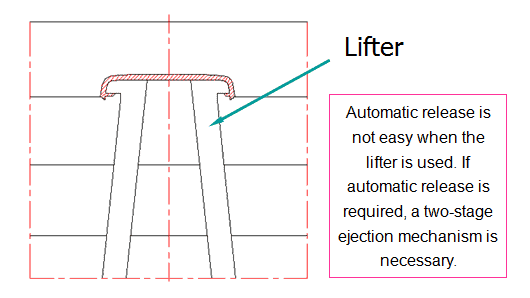
6.Lifter
When there is an undercut on the inner surface of the side wall of a product or the inner surface on the top of a product, the lifter is used. How it works: While ejecting the product, it is limited by the inclined surface and thus moves laterally at the same time, so that the product is released.
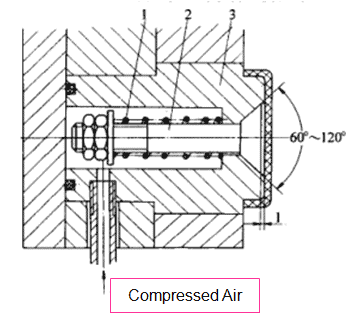
7. Air Ejection
Air ejector refers to a mechanism that introduces compressed air between the product and the mold through the air valve installed in the mold to eject the product. The pressure of compressed air usually stands at 0.5 to 0.6 MPa.
Ejected by center valve pressure
Scope of application: Release of large-size, deep-cavity and thin-walled containers, but mostly used to support other ejector types.
Features: The mold structure is greatly simplified, and the product can be ejected at any location when the mold opens.