What is PBT?
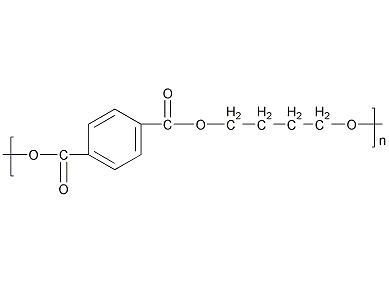
Polybutylene terephthalate, Abbr. PBT, falls into the polyester series. It is a milky white, translucent or opaque crystalline thermoplastic polyester resin polymerized from 1.4-pbt butylene glycol (1.4-butylene glycol) and purified terephthalic acid (PTA) or dimethyl terephthalate (DMT), before going through a mixing process. It is collectively referred to as thermoplastic polyester, or saturated polyester together with PET.
It is not easy to burn, no liquid drips
during burning, and the fire goes out within 5 seconds after the flame is
removed (similar to PC).
PBT is one of the toughest engineering thermoplastic materials. It is a semi-crystalline material with great chemical stability, mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties, as well as outstanding thermal stability. The materials possess very good stability under a wide range of environmental conditions. PBT features a very low hygroscopicity. The tensile strength of the non-reinforced PBT is 50MPa, while that of the glass additive reinforced PBT is 170MPa. However, too much glass additive will cause the material to become brittle. PBT crystallizes very fast, which tends to cause bending deformation due to uneven cooling. For materials with glass additives, the shrinkage in the flow direction is able to be reduced, but the shrinkage in the direction vertical to the flow is basically the same as that of common materials. Usually, the shrinkage of PBT ranges between 1.5% and 2.8%, and that of 30% glass additive reinforced PBT is between 0.3% and 1.6%. The melting point (225°C) and deformation temperature of PBT are lower than those of PET. Its Vicat softening point is approximately 170°C, and glass transition temperature is between 22°C and 43°C. Due to the high crystallization speed of PBT, its viscosity is extremely low, while the cycle time of PBT parts is usually also very short.

Injection Molding conditions of PBT
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a
general-purpose engineering plastic with a very mature polymerization process,
a low cost, and an easy molding process. Unmodified PBT has unsatisfactory properties,
so it needs to be modified in practical applications. Among them, glass fiber
reinforced PBT accounts for more than 70% of the material.
1. Process Characteristics of PBT
PBT has a clear melting point, i.e., 225-235℃. It is a crystalline material, with
a crystallinity of up to 40%.
The viscosity of the PBT melt is not as
affected by temperature as shear stress. Therefore, during plastic injection
molding, injection pressure has a very obvious influence on the fluidity PBT
melt.
PBT features great fluidity and low
viscosity in the molten state, second only to nylon, so it is prone to the “casting”
phenomenon during injection molding.
Molded PBT products are anisotropic.
PBT is easily degraded in water at high
temperatures.
2. Injection Molding Machine
When selecting the screw injection molding
machine, pay attention to the following considerations:
- The material consumption of the
product should be controlled within 30%-80% of the rated maximum injection
volume of the injection molding machine. It is not appropriate to use a large
injection molding machine to produce small-sized products. - Gradient three-section screw
should be selected, with a length to diameter ratio of 15-20 and a compression
ratio of 2.5-3.0. - Self-locking nozzles equipped
with heater and temperature controller should be selected. - When molding the flame
retardant PBT, the relevant parts of the injection molding machine should be
treated with anticorrosion.
3. Product and Mold Design
① The product should
not be too thick. PBT is very sensitive to notch, so the transition on the
product such as the right angles should be connected with a circular arc.
② The molding
shrinkage of PBT is relatively high, ranging from 1.7% to 2.3%, so the mold
must be designed a certain draft angle.
③ The mold
needs to be designed with venting holes or grooves.
④ The gate diameter
should be large enough.
⑤ The mold
needs to be equipped with a temperature controller. The maximum mold temperature
cannot exceed 100℃.
⑥ When molding
flame retardant PBT, the mold surface should be chrome plated, so as to prevent
corrosion.
4. Raw Material Preparation
Before injection molding, PBT should be
dried to keep the moisture content below 0.02%. When a hot air circulation drier
is used, the corresponding drying time should not exceed 8h, 5h and 3h for 105℃, 120℃
and 140℃.
5. Injection Molding Parameters
① Injection
temperature – the decomposition temperature of PBT is 280℃, so in actual production, it is usually
controlled between 245-260℃.
② Injection
pressure – the injection pressure is usually 50-100MPa.
③ Injection speed
– PBT cools down very fast, so a faster injection speed should be adopted.
④ Screw speed &
backpressure – the screw speed for PBT should not exceed 80rpm, usually between
25 and 60rpm, while the backpressure is usually 10% to 15% of the injection
pressure.
⑤ The mold
temperature is usually controlled at 70-80℃, and the temperature difference among all areas does not exceed 10℃.
⑥ The molding
cycle is usually 15-60s.
6. Key Considerations
① Use of
recycled material – the ratio of recycled material to new material is usually
25% to 75%.
② Use of
release agent – usually, the release agent is not used. When necessary,
silicone release agent is selected.
③ Machine Shutdown
– polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a general-purpose engineering plastic
with a very mature polymerization process, a low cost, and an easy molding
process. Unmodified PBT has unsatisfactory properties, so it needs to be
modified in practical applications. Among them, glass fiber reinforced PBT
accounts for more than 70% of the material.
