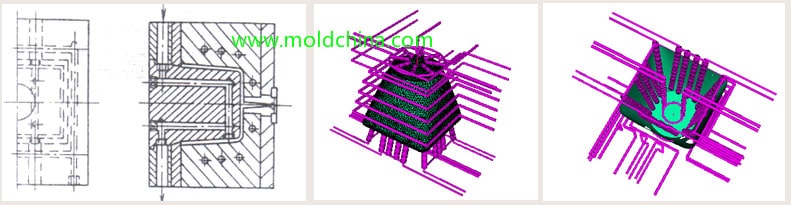
During the plastic injection molding process, the mold temperature directly determines the plastic product quality and the molding efficiency. An excessively high mold temperature not only extends the cooling time and reduces production efficiency, but also causes the plastic melt to lose its original performance; an excessively low mold temperature affects the melt fluidity and warps the plastic product. Therefore, in order to obtain high-quality and high-efficiency plastic products, it is necessary to strictly control the mold temperature. The design purpose of the injection mold cooling system is to cool the mold through a temperature-regulating medium, and take away the excess heat in the mold, so that the mold is always able to maintain the required temperature, thereby ensuring the quality of plastic products.
How the molding of plastic products is influenced by the injection mold cooling system is mainly reflected in the following 4 aspects:
1. Molding cycle. A key step to improve the productivity is to reduce the molding cycle. During the plastic injection molding process, the melt temperature in the mold is usually maintained at about 200-300°C, and the temperature when they are ejected is usually below 60-80°C, of which about 5% of the heat is dissipated to the atmosphere through mold conduction and convection. The majority part of the heat needs to be taken away by mold cooling system through the coolant, and the cooling time accounts for about 50% to 80% of the molding cycle. Therefore, the cooling system for injection molds plays a very important role in improving the overall production efficiency.
2. Moldability. During the plastic injection molding process, temperature parameters need to be strictly controlled to keep a stable mold temperature. A proper cooling system is able to keep the temperature of each mold part uniform, reduce product warpage, improve product surface quality, and ensure production efficiency.
3. Dimensional accuracy. Generally speaking, for crystalline plastics, the higher the mold temperature, the more favorable it is for the crystallization to proceed sufficiently, so as to prevent easy size changes. For softer plastics, the lower the mold temperature, the better the dimensional accuracy. However, no matter what kind of plastic material is used, it is necessary to maintain a constant mold temperature through the cooling system, thus reducing the fluctuations in plastic product shrinkage.
4. Mechanical properties. During the plastic injection molding process, a proper cooling system design is able to effectively improve the temperature field inside the mold and reduce the internal stress of the plastic product, thus enhancing its mechanical properties.
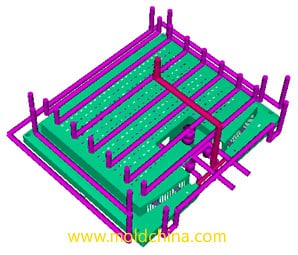
Design Principles of Cooling System
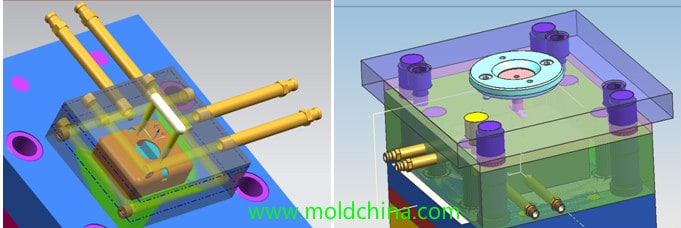
The distance from the wall of the cooling channel to the surface of the cavity should be kept as identical as possible, usually between 15mm and 25mm.
Maximize the number of cooling channels and make it easy to process. The diameter of the cooling channel we choose is Ф8.0, and the distance between two parallel channels is 30mm.
The gating system often comes in contact with the nozzle of the injection molding machine, while the molten plastic is first injected from the gate, so the gate is where the highest mold temperature is. In order to ensure a balanced mold temperature, the cooling channel should first pass through the gate, because the coolant should flow from high-temperature to low-temperature areas.
Water leakage should be prevented in the cooling system. Therefore, when the cooling channel has to pass through mold plate joints, good sealing measures must be ensured.
In the circulating cooling channel, the cooling paths of the coolant should be of the same length.
The coolant inlet and outlet should be located in areas that doesn’t affect operation
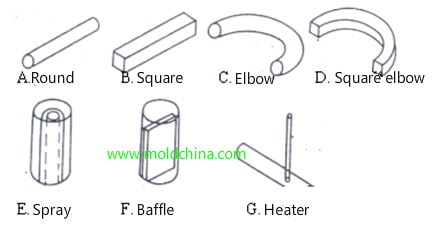
Basic Cooling Channel Types and Specs
Basic cooling channel types are shown below. A and F are the commonly used ones.
Cooling channel specs and its relationship with product thickness:

The basic forms of mold cooling systems
1)cooling systems in mold base
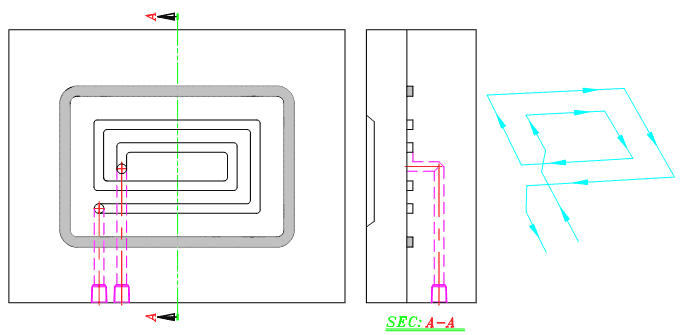
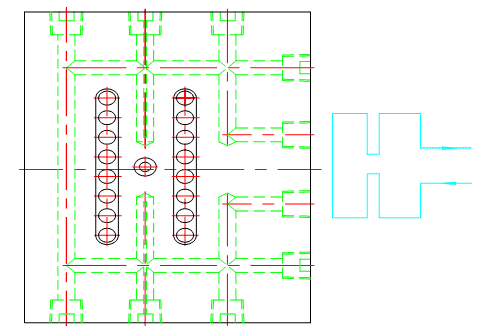
2)cooling in cavity and core inserts


3)Cooling through mold base and main inserts
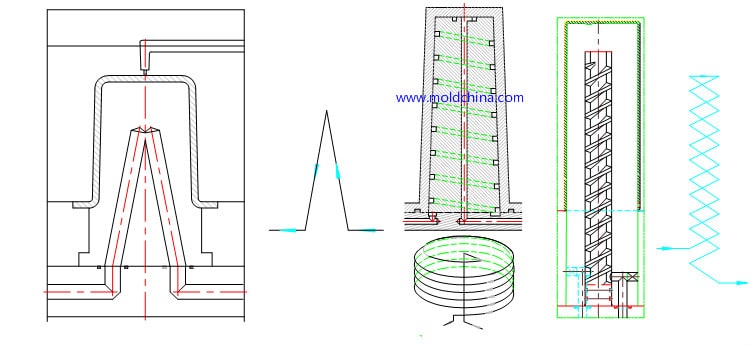
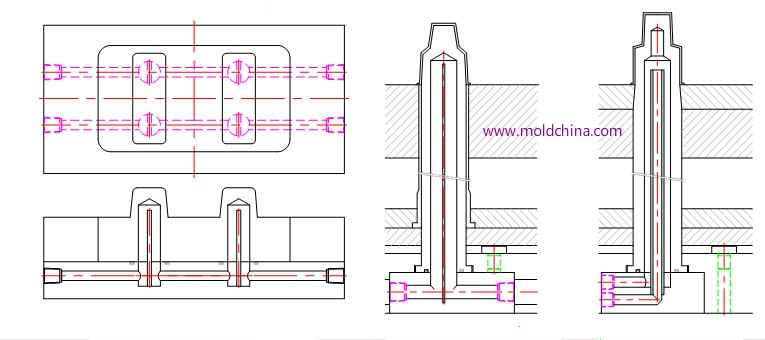
4)Mold cooling follow product shape